Language Delay: Types, Symptoms And Causes
Communication is what has driven the great developments of the human being, but not everyone can develop that capacity properly. We tell you more about the possible language delays that arise in childhood.
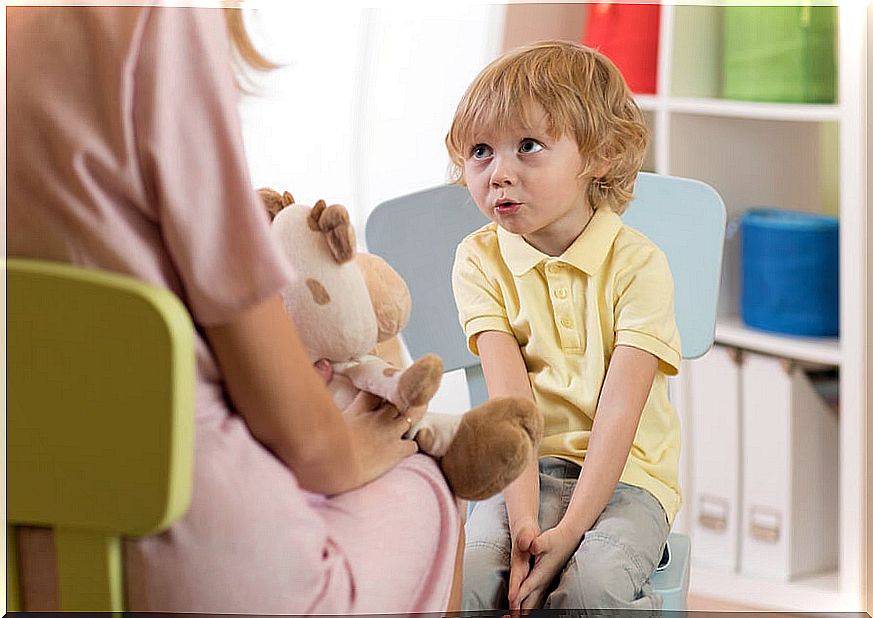

From birth, babies begin to communicate by crying or smiling. As they grow, they incorporate gestures and sounds, until they emit their first words. However, m uchos have delayed language for different reasons and have difficulty expressing themselves and sometimes to understand.
Communication delay can affect children’s interactions, character, and learning, however, it is not an uncommon condition. Between 5 and 10% of school-age children have some kind of communication problems, according to the Department of Health at the University of Michigan (United States).
Language delay: a problem in communication
Types and symptoms
There are two types of language delay : receptive delay, which refers to the difficulty of understanding what is being communicated to you, and expressive delay, which is the difficulty of communicating with words. On many occasions the two are combined.
Sometimes it takes some time to discover these communication difficulties, but there are symptoms that can draw the attention of parents to suspect a problem.
- At around 15 months they do not babble.
- They do not speak words by 2 years.
- They have trouble expressing sentences when they are around 3 years old.
- They don’t understand instructions.
- They do not react when spoken to.
Causes of language delay
Speech delay usually originates in the brain, but can sometimes be caused by a physical impairment, social adjustment problems, or learning difficulties.
The main causes are:
- Hearing loss. It is common for children who cannot hear to have a hard time learning to speak.
- Autism. Not all autistic children have trouble expressing themselves, but speech problems are sometimes caused by autism.
- Neurological problems. Conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscle atrophy can affect the muscles needed to speak.
- Dysfunctional environments. Homes in which children feel marginalized, attacked, or isolated can make it difficult for them to learn to speak. Sometimes in these cases, the lack of communication is selective.
- Apraxia of language. This is a condition in which the speech muscles do not react to the signal from the brain.
Treatment
Sometimes it is difficult to know if the delay in the language is due to one of these conditions or is simply a temporary situation. The most indicated is to consult with the pediatrician if one notices that the child does not comply with the normal communication cycles. A timely diagnosis can help a prompt solution.
Depending on the cause, a child with a language delay may be referred to an audiologist, speech therapist, psychologist, or even a social worker. The most advisable thing is to have a multidisciplinary team in which the communication of the child is stimulated.
Family involvement is essential to the success of any therapy. Whether it is to stimulate language or to establish non-oral forms of communication, parents must be involved in the whole process.
Tips for parents
From the moment they are born, children begin to learn everything that their new environment presents to them. One of his first references is the auditory one. Even when they are in the womb, at 18 months, they begin to hear the first sounds and at 25 or 26 weeks they can respond to voices with movements.
Therefore, it is recommended to speak to them from the moment they are born or before. Other stimuli, as they grow, will aid in the rapid development of their communication skills.
- Respond to their babbling with words and sounds.
- Sing to them since they are babies.
- Read books aloud to them. You can start with special books for babies and progress as they grow.
- Always answer your questions.
- Teach them the names of things, even since they are babies and still do not speak.
Finally, if you have detected a problem in your child’s communication, consult a specialist on the subject. As we have mentioned, an early diagnosis will help to include an adequate therapy with which to solve language problems.